Answer:
Explanation:
Let D stand for a defective unit,
G for a good unit.
Y can only be 2, 3, or 4.
P(Y=2):
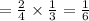
Need to have D, D. There are 2 Ds of 4 total to start, then presuming the first was a D, there is 1 D of 3 total for the second choice.
P(Y=3):
Need to have D,G,D or G,D,D
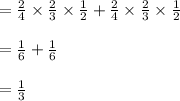
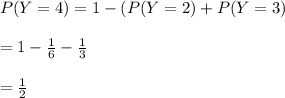
So:
P(Y=2) = 1/6
P(Y=3) = 1/3
P(Y=4) = 1/2
P(Y=n) = 0 for all other values of n