Answer:
t = 47 years
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the number of years in which the electrons cross the complete transmission, you first calculate the drift velocity of the electrons in the transmission line, by using the following formula:
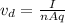 (1)
(1)
I: current = 1,010A
A: cross sectional area of the transmission line = π(d/2)^2
d: diameter of the transmission line = 2.00cm = 0.02 m
n: free charge density = 8.50*10^28 electrons/m^3
q: electron's charge = 1.6*10^-19 C
You replace the values of all parameters in the equation (1):
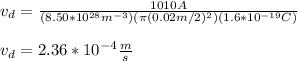
with this value of the drift velocity you can calculate the time that electrons take in crossing the complete transmission line:
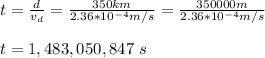
Finally, you convert this value of the time to years:
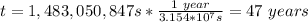
hence, the electrons take around 47 years to cross the complete transmission line.