Answer:
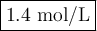
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) Balanced equation
2NaOH + H₂SO₄ ⟶ Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
(b) Moles of H₂SO₄
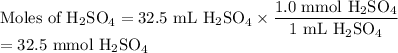
(c) Moles of NaOH
The molar ratio is 2 mol NaOH:1 mol H₂SO₄.
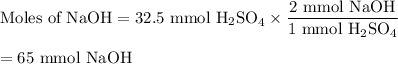
(d) Molar concentration of NaOH

Note: The answer can have only two significant figures because that is all you gave for the molar concentration of the sulfuric acid.