Answer:
Here's what I get
Step-by-step explanation:
(i) Voltaic cell
A voltaic cell is a device that uses a chemical reaction to produce electrical energy.
(ii) Overall Cell Potential
The standard reduction potentials for the half-reactions are
ℰ°/V
Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ Cu 0.34
Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ Zn -0.76
The half-reaction with the more positive potential is the reduction half-reaction. It is the reaction that occurs at the cathode.
The half-reaction with the more negative potential is the oxidation half-reaction. It is the reaction that occurs at the anode.
We reverse that half-reaction and subtract the voltages to get the cell reaction.
ℰ°/V
Cathode: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ Cu 0.34
Anode: Zn ⇌ Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ -0.76
Cell: Zn + Cu²⁺ ⇌ Zn²⁺ + Cu 1.10
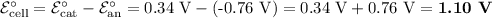
(iii) Diagram
The specific labels will depend on your textbook.
They are often as follows.
a. Electron flow
b. Voltmeter or lightbulb
c. Electron flow
d. Cathode or Cu
e. Cu²⁺(aq) and NO₃⁻(aq)
f. Salt bridge
g. Zn²⁺(aq) and NO₃⁻(aq)
h. Anode or Zn
The salt bridge enables ions to flow in the internal circuit and to maintain electrical neutrality in the two compartments.
It often consists of a saturated solution of KCl.
As Zn²⁺ ions form in the anode compartment, Cl⁻ ions move in to provide partners for them.
As Cu²⁺ ions are removed from the cathode compartment, K⁺ ions move in to replace them.