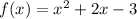Answer:
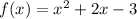
Explanation:
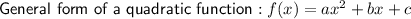
Equation 1
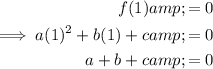
Equation 2
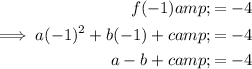
Equation 3
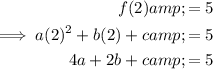
Add Equation 1 and Equation 2:
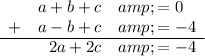
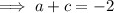
Substitute
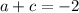 into Equation 1 and solve for b:
into Equation 1 and solve for b:
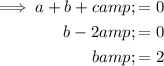
Substitute
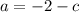 and
and
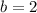 into Equation 3 and solve for c:
into Equation 3 and solve for c:

Substitute found value of c into
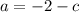 and solve for a:
and solve for a:
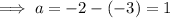
Therefore, a = 1, b = 2 and c = -3
Substitute the found values into the general form of a quadratic function to form the final equation: