Answer:
a) 4.681*10^10 electrons
b) 3.67*10^12 electrons
Step-by-step explanation:
The amount of electrons in a charge of 1C is:
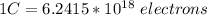
You use the previous equality as a conversion factor.
a) The sing of the charge is not important in the calculation of the number electrons, so, you use the absolute value of the charge
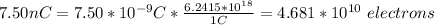
In 7.50nC there are 4.61*10^18 electrons
b)
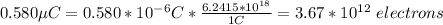
To obtain a charge of 0.580 µC in a neutral object you need to take out 3.67*10^12 electrons