Answer:
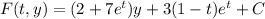
Explanation:
You have the following differential equation:
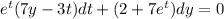
This equation can be written as:
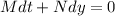
where
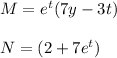
If the differential equation is exact, it is necessary the following:
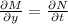
Then, you evaluate the partial derivatives:
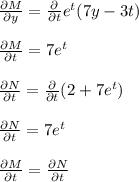
The partial derivatives are equal, then, the differential equation is exact.
In order to obtain the solution of the equation you first integrate M or N:
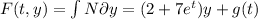 (1)
(1)
Next, you derive the last equation respect to t:
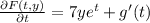
however, the last derivative must be equal to M. From there you can calculate g(t):
![(\partial F(t,y))/(\partial t)=M=(7y-3t)e^t=7ye^t+g'(t)\\\\g'(t)=-3te^t\\\\g(t)=-3\int te^tdt=-3[te^t-\int e^tdt]=-3[te^t-e^t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/df3wuni6q7227px0u9dhsvmrymd6k2508f.png)
Hence, by replacing g(t) in the expression (1) for F(t,y) you obtain:
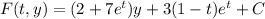
where C is the constant of integration