Answer:
Volume, V2 at STP = 818.61ml.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the following parameters;
Volume, V1 = 1140ml
Volume, V2 =?
Temperature, T1 = 37ºC to Kelvin = 273+37 = 310K
Temperature, T2 = 273K is the standard temperature.
Pressure, P1 = 82.6kPa
Pressure, P2 = 101.3kPa is the standard pressure.
To solve for volume at standard temperature and pressure (STP), we would use the combined gas law;
The combined gas law is a combination of the other three gas laws, namely Gay Lusac's law, Boyle's law and Charles's law.
Combined gas law states that the ratio of the product or multiplication of volume and pressure to the temperature of a gas is equal to a constant.
Mathematically,
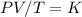
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
Let's make V2 to the subject formula;
Cross multiplying gives,
P1V1T2 = P2V2T1
Hence,
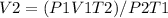
Substituting the parameters;
V2 = (82.6*1140*273)/101.3*310
V2 = 25706772/31403
V2 = 818.61ml.