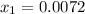Answer:
The meole fraction of acetone in the outlet liquid is
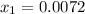
Step-by-step explanation:
1.
The schematic diagram to represent this process is shown in the diagram attached below:
2.
the mole fraction of acetone in the outlet liquid is determined as follows:
solute from Basis Gas flow rate
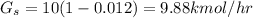
Let the entering mole be :
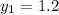 % = 0.012
% = 0.012
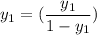
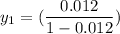
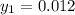
Let the outlet gas concentration be
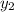 = 0.1% = 0.001
= 0.1% = 0.001
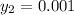
Thus; the mole fraction of acetone in the outlet liquid is:
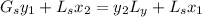
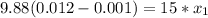
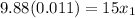
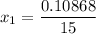
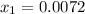
The mole fraction of acetone in the outlet liquid is