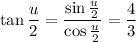Recall the double/half angle formulas:
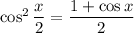
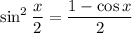
We're given
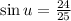 , and since
, and since
 is between π/2 and π, we expect
is between π/2 and π, we expect
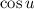 to be negative. So from the Pythagorean identity, we find
to be negative. So from the Pythagorean identity, we find
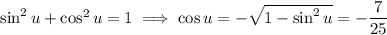
Also, we know
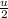 will fall between π/4 and π/2, so both
will fall between π/4 and π/2, so both
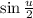 and
and
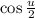 will be positive. Then we find
will be positive. Then we find
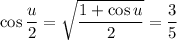
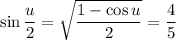
and it follows that