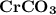Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The total mole of
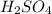 added = 15 × 1 × 10⁻³
added = 15 × 1 × 10⁻³
= 15 × 10⁻³ mole
= 15 mmoles
the number of moles of NaOH added in order to neutralize the excess acid = 0.5905 × 29.393 = 17.36 mmoles
the equation for the reaction is:
2NaOH +
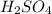 -------->
-------->
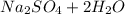
i.e
2 moles of NaOH react with
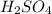
1 moles of NaOH will react with 1/2
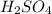
17.36 mmoles of NaOH = 1/2 × 17.36 mmoles of
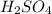
= 8.68 mmoles
Number of moles of
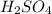 that react with MCO₃ = Total moles of
that react with MCO₃ = Total moles of
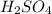 added - moles of
added - moles of
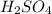 reacted with NaOH
reacted with NaOH
= (15 - 8.68) mmoles
= 6.32 mmoles
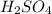 +
+
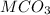 ------>
------>
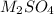 +
+
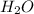 +
+
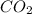
1 mole of
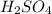 react with 1 mole of
react with 1 mole of
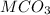
6.32 mmoles of
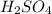 = 6.32 mmoles of
= 6.32 mmoles of
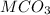
number of moles of
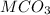 = 6.32 10⁻³ moles
= 6.32 10⁻³ moles
mass of
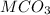 (carbonate salt) = 0.533 g
(carbonate salt) = 0.533 g
molar mass of
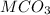 = (M+60)g/mol
= (M+60)g/mol
We all know that ;
number of moles = mass/molar mass
Then:
6.32 10⁻³ = 0.533 / (M+60)
(M+60) = 0.533/ 6.32 10⁻³
M + 60 = 84.34
M = 84.34 - 60
M = 24.34
Thus the element with the atomic mass of 24.34 is Chromium
The chemical formula for the compound is :