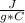Answer:
The specific heat of the material is 0.2
Step-by-step explanation:
Calorimetry is the measurement and calculation of the amounts of heat exchanged by a body or a system.
In this way, there is a direct proportional relationship between heat and temperature (Two magnitudes are directly proportional when there is a constant so that when one of the magnitudes increases, the other also; and the same occurs when one of the two decreases .). The constant of proportionality depends on the substance that constitutes the body as on its mass, and is the product of the specific heat for the mass of the body. So, the equation that allows calculating heat exchanges is:
Q = c * m * ΔT
Where Q is the heat exchanged by a body of mass m, made up of a specific heat substance c and where ΔT is the temperature variation.
Then, the amount of heat received or transferred by a body when it undergoes a temperature variation (Δt) without there being a change of physical state (solid, liquid or gaseous) is calculated using the previously expressed equation.
In this case:
- Q= 75 J
- c=?
- m=15 g
- ΔT=Tfinal - Tinitial= 40 °C - 15 °C= 25 °C
Replacing:
75 J= c*15 g*25°C
Solving:
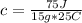
c= 0.2
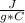
The specific heat of the material is 0.2