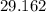Answer:
Equilibrium constant is equal to
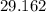
Step-by-step explanation:
If the reaction is of this form
aA(g) + bB(g) ⇄ cC(g) + dD(g)
Then , the Kp of this equation will be equal to
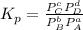
Given
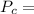
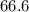 MPa and c is equal to two
MPa and c is equal to two
 MPa
MPa
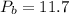 MPa
MPa
Here a and b is equal to zero.
Substituting the given values we get -
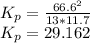
Equilibrium constant is equal to