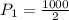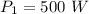Answer:500 W
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
When length is L power dissipated is
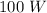
Potential difference applied is
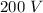
Resistance of wire is directly proportional to length of wire
Suppose initially Resistance is R
When L changes to
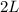
Resistance changes to
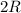
Initial Power dissipated is
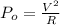
For 2 R resistance and same voltage, Power dissipated is
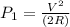
So
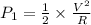
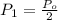
So