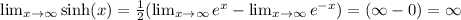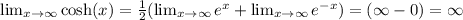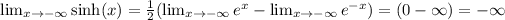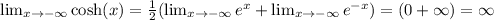Answer:
y-incercepts:
sinh(x):0, cosh(x)=1
Limits:
positive infinity: sinh(x): infinity, cosh(x): infinity
negative infinity: sinh(x): - infinity, cosh(x): infinity
Explanation:
We are given that
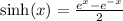
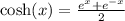
To find out the y-incerpt of a function, we just need to replace x by 0. Recall that
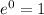 . Then,
. Then,
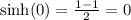
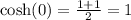
For the end behavior, recall the following:
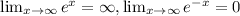
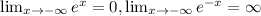
Using the properties of limits, we have that