Final Answer:
1) Representar gráficamente la trayectoria parabólica de la pelota en GeoGebra o una aplicación móvil.
2) La función cuadrática que modela la situación podría ser
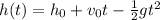 , donde
, donde
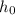 es la altura inicial,
es la altura inicial,
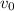 es la velocidad inicial y ( g ) es la aceleración debida a la gravedad. Las coordenadas del vértice
es la velocidad inicial y ( g ) es la aceleración debida a la gravedad. Las coordenadas del vértice
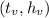 representan el tiempo y altura máxima de la parábola. Las intersecciones con el eje ( x ) son los tiempos en los que la pelota toca el suelo, y las intersecciones con el eje ( y ) indican la altura inicial y final.
representan el tiempo y altura máxima de la parábola. Las intersecciones con el eje ( x ) son los tiempos en los que la pelota toca el suelo, y las intersecciones con el eje ( y ) indican la altura inicial y final.
Explanation:
In the first step, we are tasked with graphically representing the parabolic trajectory of the ball using GeoGebra or a mobile application. This visual representation allows for a clear depiction of the ball's path, facilitating a better understanding of its motion.
Moving on to the second step, a possible mathematical expression to model the scenario is
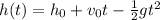 . Here,
. Here,
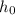 denotes the initial height,
denotes the initial height,
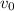 represents the initial velocity, and ( g ) is the acceleration due to gravity. The coordinates of the vertex
represents the initial velocity, and ( g ) is the acceleration due to gravity. The coordinates of the vertex
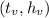 provide crucial information, indicating the time and maximum height of the parabola. The intersections with the ( x )-axis correspond to the moments when the ball makes contact with the ground, while the intersections with the ( y )-axis signify the initial and final heights.
provide crucial information, indicating the time and maximum height of the parabola. The intersections with the ( x )-axis correspond to the moments when the ball makes contact with the ground, while the intersections with the ( y )-axis signify the initial and final heights.
Understanding these mathematical concepts is fundamental in physics, enabling the accurate modeling of projectile motion. GeoGebra or similar tools enhance the learning experience by providing a dynamic and interactive platform for exploring mathematical models visually. This process not only aids in comprehending the specific scenario but also reinforces broader skills in mathematical modeling and problem-solving.