Answer: AB is approximately 8.3
Explanation:
Triangle ACD
AC = 5 (hypothenuse or side c)
CD = 4 (side a)
AD = ? (side b) 3
∠D = 90º
∠A = ?º 53º
∠C = ?º 37º
---------------------------------------------------------
Let's solve using the pythagorean theorem.
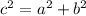
Solve for b;
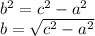
Plug in your values.
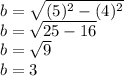
---------------------------------------------------------
Now let's find the angles.
To find ∠A, we can use tangent.
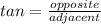
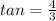
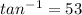
----------------------------------------------------------
In order to find ∠C, we can use an equation. We know that the sum of the angles of a triangle must be equal to 180º. Let x be ∠C
90º+53º+x=180º
143º+x=180º
Subtract 143º
x=180º-143º
x=37º
-----------------------------------------------------------
Now, let's do Triangle BCD
BC = ? (hypothenuse or side c) 6.6
CD = 4 (side a)
BD = ? (side b) 5.3
∠C = 53º
Both triangles form a 90º angle on ∠C. If ∠C in the other triangle is 37º and it forms a 90º angle, we can subtract 37º from 90º in order to find the value of the angle in triangle BCD.
90º-37º=53º
∠D = 90º
Triangle ACD and BCD have a supplementary angle D, that is how I conclude ∠D = 90º
And, to find ∠B, simply use another equation.
90º+53º+x=180º
143º+x=180º
x=180-143º
x=37º
∠B = 37º
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You may be wondering why I needed to calculate all of that if what we are trying to find is AB; the reason why is because we do not have the sides of the triangle BCD and therefore, we must use trigonometric functions to find them.
Let's begin by finding the adjacent side (or side b) in respect with ∠B
Remember, the trigonometic function that relates opposite and adjacent sides is tangent.
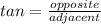
Solve for adjacent;
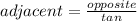
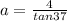
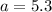
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Since we have side a and side b, we can use the pythagorean theorem to find side c or hypothenuse.
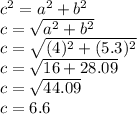
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Finally, we can add side AD and BD to find AB
AD = 3
BD = 5.3
3+5.3=8.3