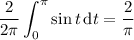The average velocity over the interval [0, 2π] is equal to the average value of v (t ) over the same interval:
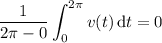
(since sin(t ) has a period of 2π)
Speed is the magnitude of velocity, or |v (t )| (the absolute value of v ). So the average speed over [0, 2π] is
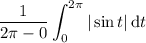
sin(t ) is positive for t between 0 and π, and negative between π and 2π. So the integral above is equal to
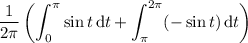
Recall that sin(t - π) = -sin(t ), so the above becomes
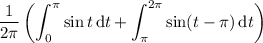
Replacing t - π with t shifts the interval of integration for the second integral to [0, π], so really we end up with