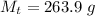Answer:
The mass of the surrounding is
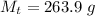
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The mass of
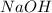 is
is
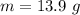
The mass of water is
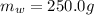
The chemical equation for the dissociation process is
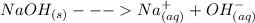
The specific heat capacity of the mixture is
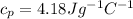
The combined mass of the solution is
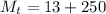
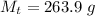
The mass of the surround here is the mass of the coffee-cup calorimeter and this contain the mixture ( water and the NaOH ) so the mass of the surrounding is