Answer:
Specific heat capacity of aluminium is 0.869J/g°C
Step-by-step explanation:
Values: 51.1g of Al, 150.0g of water, Aluminium sample: 92.1°C; Water: 18.0°C, final temperature: 22.9°C.
The heat absorbed for the water is the same relased for the aluminium, the formula is:
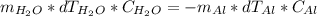
Where m is mass, dT is change in temperature and C is specific heat of each compound (4.18J/g°C for water)
Replacing:
150.0g×(22.9°C-18.0°C)×4.18J/g°C = -51.1g×(22.9°C-92.1°C)×C(Al)
3072.3J = 3536.12g°C×C(Al)
0.869J/g°C = C(Al)
Specific heat capacity of aluminium is 0.869J/g°C