Answer:
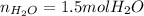
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the undergoing chemical reaction is:
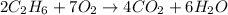
Next, we identify the limiting reactant by computing the available moles of ethane and the moles of ethane consumed by 60.0 grams of oxygen:
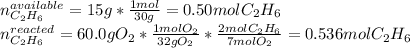
Thus, we notice there are less available moles, for that reason, the ethane is the limiting reactant. Finally, we can compute the produced moles of water by:
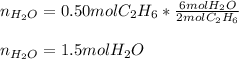
Best regards.