Answer:
a) Warmer
b) Exothermic
c) -10.71 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction:
KOH(s) → KOH(aq) + 43 kJ/mol
It is an exothermic reaction since the reaction liberates 43 kJ per mol of KOH dissolved.
Hence, the dissolution of potassium hydroxide pellets to water provokes that the beaker gets warmer for being an exothermic reaction.
The enthalpy change for the dissolution of 14 g of KOH is:
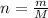
Where:
m: is the mass of KOH = 14 g
M: is the molar mass = 56.1056 g/mol
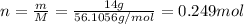
The enthalpy change is:
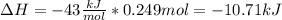
The minus sign of 43 is because the reaction is exothermic.
I hope it helps you!