Answer:
The new volume is 1.62 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law says:
"The volume occupied by a given gas mass at constant temperature is inversely proportional to the pressure." It is expressed mathematically as:
Pressure * Volume = constant
o P * V = k
Charles's law is a law that says that when the amount of gas and pressure are kept constant, the ratio between volume and temperature will always have the same value:
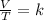
Gay-Lussac's law indicates that when there is a constant volume, as the temperature increases, the gas pressure increases. And when the temperature is decreased, the gas pressure decreases. So this law indicates that the quotient between pressure and temperature is constant.
Gay-Lussac's law can be expressed mathematically as follows:
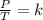
Combined law equation is the combination of three gas laws called Boyle's, Charlie's and Gay-Lusac's law.
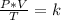
Having an initial state 1 and a final state 2 it is possible to say that:
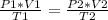
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) indicate pressure conditions P = 1 atm and temperature T = 0 ° C = 273 ° K. Then:
- P1= 1 atm
- V1= 1.2 L
- T1= 273 °K
- P2= 0.80 atm
- V2= ?
- T2= 21°C= 294 °K
Replacing:
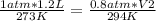
Solving:
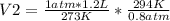
V2= 1.62 L
The new volume is 1.62 L