Answer:
(a) The shear plane angle is: ∅=26. 86°
(b) the shear strain for the operation is: γ = 2.155234
Step-by-step explanation:
In orthogonal cutting, the wedge-shaped tool used in the cutting edge is perpendicular to the direction of motion.
(a) The shear plane angle is:
shear plane angle is the angle between shear plane and the cutting velocity in orthogonal cutting.
r= t
 ÷ t
÷ t
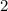
Where, t
 = Initial thickness before the cut
= Initial thickness before the cut
t
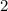 = deformed thickness
= deformed thickness
r = cutting ratio, which signifies the ratio of chip thickness of metal before cutting to the thickness after cutting.
r = 0.30 mm ÷ 0.65 mm
= 0.461538
∅ = tan∧
 ( 0.461538 cos 15 ÷ ( 1 - 0.461538 sin 15) )
( 0.461538 cos 15 ÷ ( 1 - 0.461538 sin 15) )
= tan∧
 (0.506289)
(0.506289)
∅=26. 86°
(b) the shear strain for the operation is:
Shear strain is the stress tangent of an angle, that acts parallel to a material cross section.
γ = cot 26.86 + tan (26.86 - 15)
=1.974523 + 0.210004
γ = 2.155234