Answer:
hello your question has some missing information attached to the answer is the missing component
Answer : αaxial,p = -6.034 ksi ( compressive )
αbend,p = 19.648 ksi ( tensile )
Step-by-step explanation:
αaxial, p =
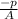 equation 1
equation 1
αbend, p =
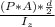 equation 2
equation 2
P = load = 35 kips
A = area of column = 5.8
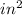
d = column cross section depth = 9.5 in
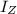 = 55.0
= 55.0
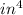
Hence equation 1 becomes
αaxial,p = -35 / 5.8 = - 6.034 ksi ( compressive )
equation 2 becomes
αbend, p =
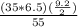 = + 19.648 ksi ( tensile )
= + 19.648 ksi ( tensile )