Answer:
To make a 3.50 M solution, 38.5 moles of solute will be needed if 11 liters of solution are required.
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is defined as a concentration unit that indicates the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. That is, it indicates the number of moles of solute that are dissolved in a given volume. Then, the molarity is calculated by dividing the moles of the solute by the liters (volume) of the solution:
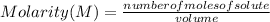
Molarity is expressed in units (
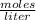 ).
).
So, knowing the definition of molarity, you can apply a rule of three as follows: if by the definition of molarity in 1 L of solution there are 3.5 moles of solute, in 11 L of solution how many moles of solute are there?
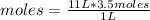
moles=38.5
To make a 3.50 M solution, 38.5 moles of solute will be needed if 11 liters of solution are required.