Answer:
(a) The mixture temperature, T₃ is 305.31 K
(b) The mixture pressure, P₃ after establishing equilibrium is 114.5 kPa
Step-by-step explanation:
Here we have the initial conditions as
Oxygen compartment
Mass of oxygen = 7 kg
Molar mass of oxygen = 32.00 g/mol
Pressure in compartment, P₁ = 100 kPa
Temperature of oxygen, T₁ = 40 °C = 313.15 K
Number of moles of oxygen, n₁ is given by
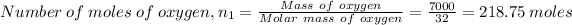
From the universal gas equation, we have;
P·V = n·R·T
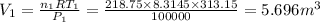
For the Nitrogen compartment, we have
Mass of nitrogen = 4 kg
Molar mass of oxygen = 28.0134 g/mol
Pressure in compartment, P₂ = 150 kPa
Temperature of oxygen, T₂ = 20 °C = 293.15 K
Number of moles of nitrogen, n₂ is given by
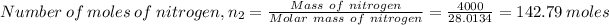
From the universal gas equation, we have;
P·V = n·R·T
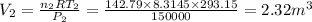
Therefore
We have for nitrogen
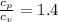
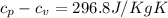
Therefore;
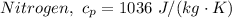
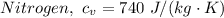
The molar heat capacities of Nitrogen are therefore as follows;
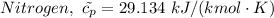
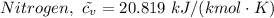
For oxygen we have
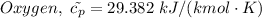
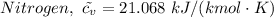
The final volume, V₃ then becomes
V₃ = V₁ + V₂ = 5.696 m³ + 2.32 m³ = 8.016 m³
(a) For adiabatic mixing of gases the final temperature of the mixture is then found as follows
Therefore before mixing
U₁ =
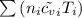 = 0.21875 × 21.068 × 313.15 + 0.14279×20.819×293.15 = 2,314.65 kJ
= 0.21875 × 21.068 × 313.15 + 0.14279×20.819×293.15 = 2,314.65 kJ
After mixing, we have
U₂ =
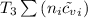 = T (0.21875 × 21.068 + 0.14279×20.819) = T×7.58137001
= T (0.21875 × 21.068 + 0.14279×20.819) = T×7.58137001
Therefore the final temperature, T is then
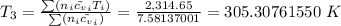
The mixture temperature, T₃ = 305.31 K
(b) The mixture pressure, P₃ after equilibrium has been established is given as
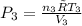
Where:
n₃ = n₁ + n₂ = 0.21875 + 0.14279 = 0.36154 kmol = 361.54 moles
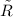 = 8.3145 J/(gmol·K)
= 8.3145 J/(gmol·K)
Therefore ,
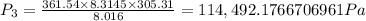
P₃ ≈ 114.5 kPa.