Answer:
the theoretical value for the number of moles of
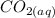 is 0.0173 moles
is 0.0173 moles
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is represented by:
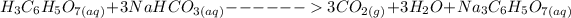
From above equation; we would realize that 3 moles of
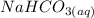 reacts with
reacts with
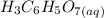 to produce 3 moles of
to produce 3 moles of
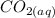
However ; the molar mass of
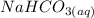 = 84 g/mol
= 84 g/mol
mass given for
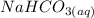 = 1.45 g
= 1.45 g
therefore , we can calculate the number of moles of
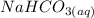 by using the expression :
by using the expression :
number of moles of
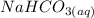 =
=
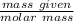
number of moles of
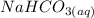 =
=
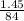
number of moles of
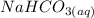 = 0.0173 mole
= 0.0173 mole
Since the ratio of
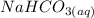 to
to
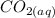 is 1:1; that implies that number of moles of
is 1:1; that implies that number of moles of
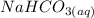 is equal to number of moles of
is equal to number of moles of
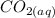 produced.
produced.
number of moles of
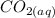 =
=
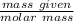
0.0173 =
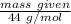
mass of
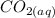 = 0.0173 × 44
= 0.0173 × 44
mass of
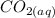 = 0.7612 g
= 0.7612 g
Thus; the theoretical value for the number of moles of
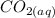 is 0.0173 moles
is 0.0173 moles