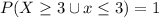Answer:
a) For this case we have the following probability distribution given:
X -1 0 2 3 4
P(X) 0.15 -0.25 0.30 0.11 0.29
XP(X) -0.15 0.25 0.60 0.14 4.29
For any probability distribution we need to satisfy two conditions:
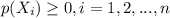
And then the value os -0.25 is not correct. The second condition is:
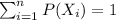
And for this case s we use 0.15+0.25+0.30+0.11+0.29 = 1.1>1 so then we need to fix this condition too. The other problems are related to the column xP(X) are incorrect. Here is an example of a probability distribution purposed
b) X -1 0 2 3 4
P(X) 0.15 0.25 0.30 0.12 0.29
And for this case the expected value would be:
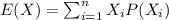
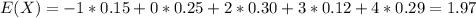
c)
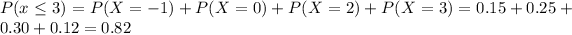
d) P(X \geq 3) = P(X=3) +P(X=4)= 0.12+0.29=0.41[/tex]
e) For this case we can use the total rule of probability and we got:
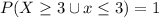
Explanation:
Part a
For this case we have the following probability distribution given:
X -1 0 2 3 4
P(X) 0.15 -0.25 0.30 0.11 0.29
XP(X) -0.15 0.25 0.60 0.14 4.29
For any probability distribution we need to satisfy two conditions:
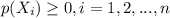
And then the value os -0.25 is not correct. The second condition is:
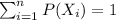
And for this case s we use 0.15+0.25+0.30+0.11+0.29 = 1.1>1 so then we need to fix this condition too. The other problems are related to the column xP(X) are incorrect. Here is an example of a probability distribution purposed
Part b
X -1 0 2 3 4
P(X) 0.15 0.25 0.30 0.12 0.29
And for this case the expected value would be:
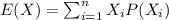
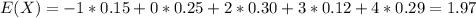
Part c
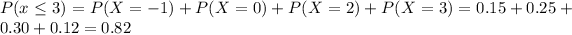
Part d
P(X \geq 3) = P(X=3) +P(X=4)= 0.12+0.29=0.41[/tex]
Part e
For this case we can use the total rule of probability and we got: