Answer:
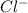
Step-by-step explanation:
The kidneys help control the level of acid in the body, removing acid from the blood and removing it in the urine. Acidic substances in the body are neutralized by alkaline substances, mainly bicarbonate.
The renal tubule is the largest portion of a nephron, the functional unit of the kidney. It has the function of modifying the composition of the ultrafiltrate produced by the glomerulus, through reabsorption and secretion processes, in order to recover useful substances and facilitate the elimination of harmful substances.
In the second part of the proximal tubule, sodium diffuses through the tight junctions between the tubular cells following the gradient of the chlorine, by which it is attracted given the opposite charge; the concentration of chlorine, in fact, increases throughout the proximal tubule and this allows the diffusion of the interstitial fluid. Alternatively, chlorine can also diffuse transcellularly.