Answer:
a)
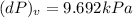
b)
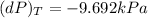
c) dP = 0 Pa
Step-by-step explanation:
The specifies equation is :
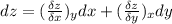
Note that:
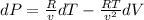
1% increase in temperature at specific volume:
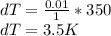
a) Change in pressure of helium at constant volume:
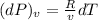
R = 2.0769 kJ/kg-K
dT = 3.5 K
v = 0.75 m³/kg
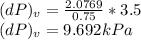
b)
dv = (1%/100%) *0.75
dv = 0.0075 m³/kg
Change in pressure of helium at constant temperature:
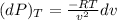
R = 2.0769 kJ/kg-K
T = 350 K
v = 0.75 m³/kg
dv = 0.0075 m³/kg
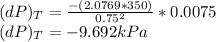
c) The change in pressure of helium :
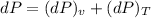
dP = 9.692 - 9.692
dP = 0