Answer:
(a) 12.25 °
(b) The acceleration magnitude will be more than 0.063·g or 0.212·g
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) Here we have
V = u + at
And KE = KE
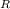 + KE
+ KE
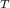 = 0.5 m·v² + 0.5 Iω²
= 0.5 m·v² + 0.5 Iω²
I = 2/3m·r², ω = v/r
KE = 0.5 m·v² + 2/3 m·r²·v/r
Therefore = 0.5 m·v² + 2/3 m·r·v
Therefore, v is reduced by
v = √(g·h·10/7) or v² = g·h·10/7 compared to v² = 2gh
If a = 0.063 g we have
v² = 0.063·g·h·10/7 = 0.09·g·h hence the height which is
v = 0.3√(g·h) and v = √(2·g·h)
Therefore, the angle is
sin⁻¹ (0.3/√2) = 12.25 °
v = u + at where
h = ut + 0.5at²
(b) At that angle, we have
h₁ = 0.5gt² and
h₂ = 0.212 × h₁
Therefore
a = 0.212 g, the acceleration will be more than 0.063·g.