Answer:
a) Calculated value F = 1.088 < 3.29
null hypothesis is accepted
Therefore there is no difference between the variances.
b) t = 8.79 > 1.746 for 16 degrees of freedom at 95% level of significance.
The null hypothesis is rejected.
we do not compare means between the two data sets
c) The 95 % of confidence intervals for the difference between means
are (3.30 ,4.68)
Explanation:
Given data
Data set A Data set B
Total 677.98 Total 574.24,
n₁= 10 n₂=8
mean((x₁⁻) = 67.798 mean( x₂⁻) = 71.78
variance(S₁²) = 0.663084 variance(S₂²)= 0.727143
S.D(S₁) = 0.814299972 S.D(S₂) = 0.8527267191
a) Null hypothesis (H₀) : σ₁² = σ₂²
Alternative hypothesis: σ₁² ≠ σ₂²
The compare of variances we will use the test statistic is F - distribution
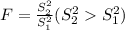
given data total= 677.98
∑(x-x⁻ )² = 677.98
Given data ∑(y-y⁻ )² = 574.24
S₁² =
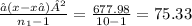
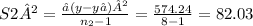
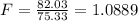
The degrees of freedom ν = ( n₁-1, n₂-1) = (10-1 ,8-1) = (9 , 7)
Tabulated value of F for (9 , 7) degrees of freedom at 5% level of significance is 3.29 (see 'F' table at 0.05 level )
Conclusion:-
Calculated value F = 1.088 < 3.677
null hypothesis is accepted
Therefore there is no difference between the variances.
b)
Null hypothesis (H₀) : μ₁ - μ₂≤ D ( given data D= 0.5 add to each data
Alternative hypothesis: μ₁ - μ₂≥ D
Sample statistic :- (x₁⁻ - x₂⁻)
Estimated standard error:-
standard error (S. e) =
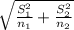
Test statistic 't'
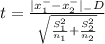
mean((x₁⁻) = 67.798 mean( x₂⁻) = 71.78
variance(S₁²) = 0.663084 variance(S₂²)= 0.727143
S.D(S₁) = 0.814299972 S.D(S₂) = 0.8527267191
standard error (S. e) =
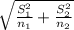 = 0.396
= 0.396
Now the test statistic
t = 8.79
The degrees of freedom of t- distribution is
ν= n₁+ n₂-2 = 10 +8-2=16
tabulated value = 1.746 for 16 degrees of freedom at 95% level of significance.
Conclusion:-
The null hypothesis is rejected.
we do not compare means between the two data sets
C) 95% of confidence interval for the difference between means
Solution:-
|(x₁⁻ - x₂⁻)| ± tₐ S. e ( (x₁⁻ - x₂⁻)
where standard error (S. e) =
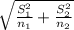
given data
mean((x₁⁻) = 67.798 mean( x₂⁻) = 71.78
variance(S₁²) = 0.663084 variance(S₂²)= 0.727143
S.D(S₁) = 0.814299972 S.D(S₂) = 0.8527267191
Standard error =
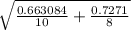 = 0.396
= 0.396
Standard error = 0.396
The degrees of freedom of t- distribution is
ν= n₁+ n₂-2 = 10 +8-2=16
tabulated value = 1.746 for 16 degrees of freedom at 95% level of significance.
The confidence intervals are
( |(x₁⁻ - x₂⁻)| - tₐ S. e ( (x₁⁻ - x₂⁻), |(x₁⁻ - x₂⁻)| + tₐ S. e ( (x₁⁻ - x₂⁻))
now substitute all values , we get
(|67.798-71.78|-1.746 X (0.396),(|67.798-71.78|+1.746 X (0.396))
on calculation we get
(3.98-0.691 ,3.98+0.691 )
(3.30 ,4.68)
The 95 % of confidence intervals for the difference between means
are (3.30 ,4.68)