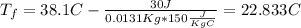Answer:
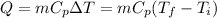
And we have the following info given:
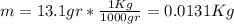
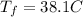 represent the initial temperature
represent the initial temperature
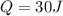 represent the heat added
represent the heat added
From tables for the platinum we know:
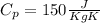
And if we solve for the initial temperature we got:
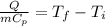
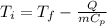
And replacing we got:
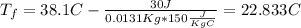
Step-by-step explanation:
For this case we can assume that the only mechanism of heat transfer is the associated to the sensible heat given by this formula:
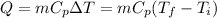
And we have the following info given:
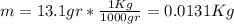
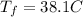 represent the initial temperature
represent the initial temperature
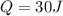 represent the heat added
represent the heat added
From tables for the platinum we know:
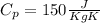
And if we solve for the initial temperature we got:
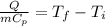
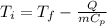
And replacing we got: