Answer:
Solution 2:
The thermal energy of any particle is given as =
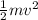
where m= Effective mass of the particle,
v= Velocity of the particle
The average kinetic energy is given as =
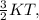
where K= Boltzmann Constant
T= Temperautre of the particle
At equilibrium,
1/2 mv² = 3/2 KT
Hence, v=
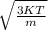
As, effective mass ratio is calculated with respect to rest mass of electron,
melectron = 0.11 * 9.11 *10-31 kg
mhole = 0.35 *9.11 *10-31 kg
K = 1.38 × 10-23 m2 kg s-2 K-1
Plotting, over a range of temperature of 0 K to 400 K, we obtain the attached Graphs (attached).
Solution 3:
The above two curves plotted are not identical as seen. From the same value of Temperature, and under identical conditons, the Thermal velocity solely depends on effective mass ratio. And it is inversely proportional to effective mass ratio. More the effective mass ratio, less the thermal velocity and flatter the slope of the curve and vice versa. As, the mass ratio of holes is more than that of electrons, the curve of electrons has a steeper slope than that of holes. Hence, the curves are not just identical.