Answer:
Yes, we have enough evidence at a 0.005 level of significance to infer that the mean score for this population exceeds 73.
Explanation:
We are given that a random sample of 10 scores on a recent chemistry exam is given below:
83, 81, 85, 87, 79, 73, 84, 86, 78, 84
You may take as known that the population is normal with a standard deviation of 13.
We have to conduct a hypothesis test to infer that the mean score for this population exceeds 73.
Let
 = mean score for this population
= mean score for this population
SO, Null Hypothesis,
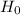 :
:
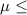 73 {means that the mean score for this population is less than or equal to 73}
73 {means that the mean score for this population is less than or equal to 73}
Alternate Hypothesis,
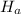 :
:
 > 73 {means that the mean score for this population exceeds 73}
> 73 {means that the mean score for this population exceeds 73}
The test statistics that will be used here is One-sample z test statistics as we know about the population standard deviation;
T.S. =
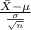 ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
where,
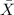 = sample mean score =
= sample mean score =
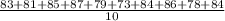 =
=
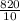 = 82
= 82
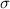 = population standard deviation = 13
= population standard deviation = 13
n = sample size = 10
So, test statistics =
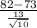
= 2.189
So, at 0.005 level of significance, the z table gives critical value of 3.8906 for one-tailed test. Since our test statistics is less than the critical value of z so we have insufficient evidence to reject null hypothesis as it will not fall in the rejection region.
Therefore, we conclude that the mean score for this population exceeds 73.