Answer: Thus 2 kg of oxygen is required in the reactants and 4 kg of sulfur dioxide in the products when 2 kg of sulfur is burned.
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical equation is:
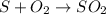
To calculate the moles :
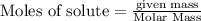
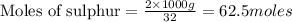
According to stoichiometry :
a) 1 mole of sulphur require = 1 mole of
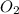
Thus 62.5 moles of sulphur will require=
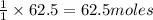 of
of
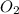
Mass of
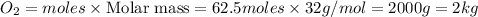
b) As 1 moles of sulphur give = 1 mole of
Thus 62.5 moles of sulphur give =
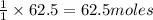 of
of
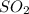
Mass of
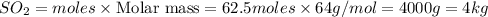
Thus 2 kg of oxygen is required in the reactants and 4 kg of sulfur dioxide in the products when 2 kg of sulfur is burned.