The answer for the following problem is mentioned below.
- Therefore the wavelength of the light is 0.468 × 10^-6 meters
Step-by-step explanation:
Energy:
The capacity to do work
Given:
frequency of the light (ν) = 6.41 × 10^14 Hz
Also given;
c = 3×10^8 m/s
h = 6.626 × 10^-34 J/s
Where,
h represents the Planck's constant
the value of h is 6.626 × 10^-34 J/s
c represents the speed of the light in the vacuum
We know;
E = h × ν
E represents the energy of the light.
E = 6.626 × 10^-34 × 6.41 × 10^14
E = 42.47 × 10^ -20 J
Given:
energy (E) = 42.47 × 10^-20 J (i.e.) from the above calculation
c = 3×10^8 m/s
h = 6.626×10^-34 J/s
We know;
E =(h×c)÷λ
λ =
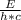
λ =
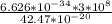
λ = 0.468 × 10^-6 m
Therefore the wavelength of the light is 0.468 × 10^-6 meters