Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Equilibrium equation
2. Equilibrium constant
The liquid substances do not appear in the expression of the equilibrium constant.
![k_c=([HBr(g)]^2)/([H_2])=4.8* 10^8M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/5ectoppymj2rvopbe101nnd0k8adm24k04.png)
3. ICE table.
Write the initial, change, equilibrium table:
Molar concentrations:
H₂(g) + Br₂(l) ⇄ 2HBr(g)
I 0.400 0
C - x +2x
E 0.400 - x 2x
4. Substitute into the expression of the equilibrium constant
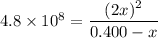
5. Solve the quadratic equation
- 192,000,000 - 480,000,000x = 4x²
- x² + 120,000,000x - 48,000,000 = 0
Use the quadratic formula:
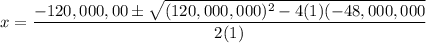
The only valid solution is x = 0.39999999851M
Thus, the final concentration of H₂(g) is 0.400 - 0.39999999851 ≈ 0.00000000149 ≈ 1.5 × 10⁻⁹M