Answer:
The probability that they have a mean height greater than 67.8 inches is 0.00212.
Explanation:
We are given that the heights of men are normally distributed with a mean of 66.8 inches and a standard deviation of 2.8 inches.
64 men are randomly selected.
Let
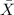 = sample mean height
= sample mean height
The z-score probability distribution for sample mean is given by;
Z =
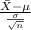 ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
where,
 = mean height = 66.8 inches
= mean height = 66.8 inches
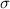 = standard deviation = 2.8 inches
= standard deviation = 2.8 inches
n = sample of men = 64
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is away from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value (area) associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X.
So, probability that they have a mean height greater than 67.8 inches is given by = P(
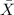 > 67.8 inches)
> 67.8 inches)
P(
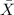 > 67.8) = P(
> 67.8) = P(
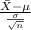 >
>
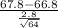 ) = P(Z > 2.86) = 1 - P(Z
) = P(Z > 2.86) = 1 - P(Z
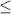 2.86)
2.86)
= 1 - 0.99788 = 0.00212
The above probability is calculated by looking at the value of x = 2.86 in the z table which has an area of 0.99788.
Therefore, if 64 men are randomly selected, the probability that they have a mean height greater than 67.8 inches is 0.00212.