Answer:
416K
Explanation:
Given:
Initial volume
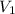 = 0.61 m^3 => 610L
= 0.61 m^3 => 610L
Final volume
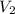 = 3.9 m^3 => 3900L
= 3.9 m^3 => 3900L
Initial temperature
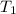 = 65 K
= 65 K
Final temperature
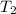 =?
=?
Charles law states that the volume of an ideal gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
Therefore,
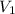 /
/
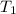 =
=
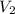 /
/
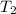
610/ 65 = 3900 /
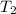
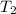 = (3900 x 65) / 610
= (3900 x 65) / 610
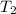 = 415.5 K ≈ 416K
= 415.5 K ≈ 416K
The final temperature of the gas is 416K