Answer:
6.33 km/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that :
A spaceprobe in outer space is flying with a constant speed
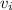 = 1.530 km/s.
= 1.530 km/s.
The probe has a payload = 1363.0 kg
which carries 3486.0 kg of rocket fuel.
Exhaust speed = 3.795 km/s
How fast will the spaceprobe travel when all the rocket fuel is used up?
As we know that the rate of change of spaceprobe momentum is equal to the thrust of the rocket.
Then;
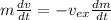
where;
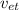 = exhaust speed
= exhaust speed
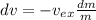
Taking the integral of the above expression; we have:
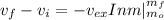
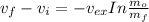
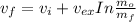
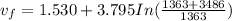
= 6.33 km/s