Step-by-step explanation:
Chemical equation for the given reaction is as follows.
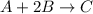
Initial : 0.6 1.30 0.5
Final : (0.6 - x) (1.30 - 2x) (0.5 + x)
It is given that at equilibrium, [A] = 0.410 M.
So, x = (0.600 - 0.410)
= 0.19 M
Hence, [B] will also be calculated as follows.
[B] =
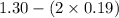
= 0.92
Now, we will calculate the value of equilibrium constant as follows.
![K_(eq) = ([C])/([A][B]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/m7yeawb5a6h9vl36rkazc288nciqna0rii.png)
=
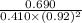
=
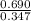
= 1.988
Thus, we can conclude that the value of the equilibrium constant,
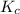 is 1.988.
is 1.988.