Answer:
(a) Vout = Vce = 5V (cut-off)
(b) Vout = 0V (saturation)
(c) Vb = - 0.6V
(d) Vb = 4.4V
Step-by-step explanation:
This transistor circuit depicts a common emitter configuration
Firstly we have to take note of the formulas used in a common - emitter configuration
- Vce = Vcc - Ic× RL
- when Ib =0, Ic= 0
- Vce = Vcc
- Taking the emitter -base circuit , we have that Ib =
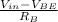
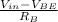
(a) when Vin = 0V, the transistor is said to be in cut-off because it does not conduct any current , In cut-off both the base- emitter and the base- collector junctions are reverse-biased.
Vce = Vcc - Ic× RL
when Ib =0, Ic= 0
Vce = Vcc
Vout = 5V
(b) Ib =
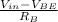 ; therefore
; therefore
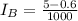
Ib = 4.4mA
Ic = β ×Ib ; this relationship does not hold good when the transistor is in saturation
therefore we have to find the value of Ic at saturation (when the transistor is on)
Ic (sat) = Vcc / RL
= 5/ 1000
= 5mA
= 10 × 4.4× 10⁻³
Ic= 0.044A; this value is too large as Ic cannot increase more than the saturation value
Vce = Vcc - Ic× RL
= 5 - 5 ×10⁻³× 1000
= 5 - 5
Vce= 0V; Vout = 0V
(c) The diagram depicts an NPN transistor ; for an NPN
the base emitter voltage Vbe = 0.6V , whereas a PNP has a Vbe = -0.6V
Vbe = Vb - Ve
Vin = Ib ×Rb + Vbe ; Ib× Rb = Vb (voltage at the base )
therefore Vin = Vb + Vbe
making Vb as the subject of formulae
Vb = Vin - Vbe
Vb = 0- 0.6 = - 0.6V
(d) when Vin = 5V
Vb = Vin - Vbe
= 5 - 0.6
Vb = 4.4V