Option D:
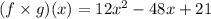 ; all real numbers.
; all real numbers.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that the functions are
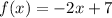 and
and
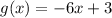
We need to determine the value of
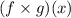 and its domain.
and its domain.
The value of
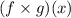 :
:
The value of
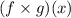 can be determined by multiplying the two functions.
can be determined by multiplying the two functions.
Thus, we have,
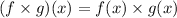
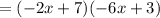
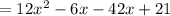
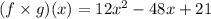
Thus, the value of
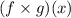 is
is
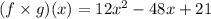
Domain:
We need to determine the domain of the function
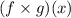
The domain of the function is the set of all independent x - values for which the function is real and well defined.
Thus, the function
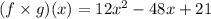 has no undefined constraints, the function is well defined for all real numbers.
has no undefined constraints, the function is well defined for all real numbers.
Hence, Option D is the correct answer.