Answer:
The magnitude of the force that each wire exerts on the other will increase by a factor of two.
Step-by-step explanation:
force on parallel current carrying wire, F = BILsinθ
where;
B is the strength of the magnetic field
L is the length of the wire
I is the magnitude of current on the wire
θ is the angle of inclination of the wire
Assuming B, L and θ is constant, then F ∝ I
F = kI
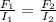
When the amount of current is doubled in one of the wires, lets say the second wire;
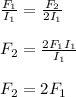
Also, if will double the amount of current on the first wire, then
F₁ = 2F₂
Therefore, the magnitude of the force that each wire exerts on the other will increase by a factor of two.