Answer:
pH=4.88
![[HCN]_(eq)=0.43699M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/2e937cjg8k0dmcll3ti49ntn3bff66lxhw.png)
![[CN^-]_(eq)=1.322x10^(-5)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a8k6l7inr3oue43ke9negkxoaimzwzlble.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the undergoing dissociation reaction is:
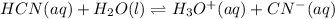
In such a way, the law of mass action becomes:
![Ka=([H^+]_(eq)[CN^-]_(eq))/([HCN]_(eq))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/3ytcitphgdti1n7ho4mpgb6wa1wkbwak6w.png)
Which in terms of the change
 due to the reaction extent, goes:
due to the reaction extent, goes:
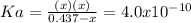
Thus, solving for
 by either quadratic equation or solver, the results are:
by either quadratic equation or solver, the results are:
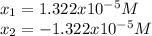
Clearly, the answer is:
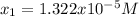
In this manner, since
 equals the concentration of hydrogen ions, the pH turns out:
equals the concentration of hydrogen ions, the pH turns out:
![pH=-log([H^+])=-log(1.322x10^(-5))=4.88](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7quwd4btci4w9inw2d6ohlz7f8m0gafobl.png)
And the concentration of the HCN and the CN⁻:
![[HCN]_(eq)=0.437M-1.322x10^(-5)M=0.43699M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/j10odkgdsq1hvzctmrrsoxpuzcxzntgv8n.png)
![[CN^-]_(eq)=1.322x10^(-5)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a8k6l7inr3oue43ke9negkxoaimzwzlble.png)
Best regards.