Answer:
-222.649 kW
Step-by-step explanation:
The first step to solve this problem is to use the first law of thermodynamics:
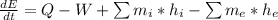
Note that Q, W, and m represent rate of heat transfer, rate of work, and mass flow rate.
This reduces to:
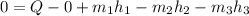
This equation can be rearranged to solve for rate of heat transfer (Q):
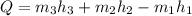
The enthalpy values for this problem can be found from tables. From Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics 9th Edition, the table used was Table A-3: Properties of Saturated Water (Liquid-Vapor): Pressure Table.
The value for
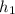 is found by using the equation
is found by using the equation
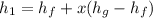
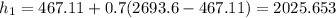 kJ/kg
kJ/kg
The value for
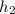 is the value for
is the value for
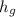 at 1.5 bar due to it being saturated vapor.
at 1.5 bar due to it being saturated vapor.
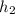 = 2693.6 kJ/kg
= 2693.6 kJ/kg
The value for
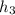 is the value for
is the value for
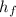 at 1.5 bar due to it being saturated liquid.
at 1.5 bar due to it being saturated liquid.
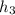 = 467.11 kJ/kg
= 467.11 kJ/kg
Now these values can be substituted back into the equation solving for Q:
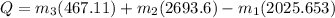
Note that
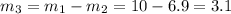 kg/s
kg/s
The equation solving for Q becomes:
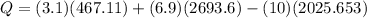
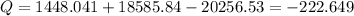 kW
kW