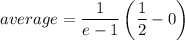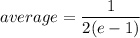Answer:
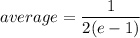
Explanation:
Average Value of a Function
Given a function g(x), we can compute the average value of g in a given interval (a,b) with the equation:
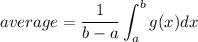
We use the given data
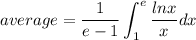
We now compute the indefinite integral with a u-substitution
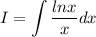
We'll use the substitution u=lnx, du=dx/x. Then
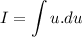
Integrating
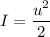
Since u=lnx
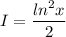
The average value is
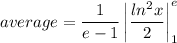
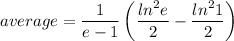
Since lne=1, and ln1=0