Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Mass, m = 62 kg, Initial speed,
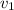 = 6.90 m/s
= 6.90 m/s
Length of rough patch, L = 4.50 m, coefficient of friction,
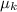 = 0.3
= 0.3
Height of inclined plane, h = 2.50 m
According to energy conservation equation,
(Final kinetic energy) + (Final potential energy) = Initial kinetic energy + Initial potential energy - work done by the friction
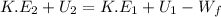
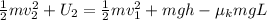
Since, final potential energy is equal to zero. Therefore, the equation will be as follows.
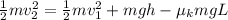
Cancelling the common terms in the above equation, we get
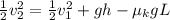
=
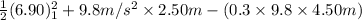
= 36.055 - 13.23
= 22.825
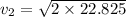
= 6.75 m/s
Thus, we can conclude that the skier is moving at a speed of 6.75 m/s when she gets to the bottom of the hill.